Amazon Web Services
Founded Year
2006About Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS) specializes in cloud computing services, offering scalable and secure information technology infrastructure solutions across various industries. It provides compute power, database storage, content delivery, and other functionalities to support the development of sophisticated applications. AWS caters to a diverse clientele, including sectors such as financial services, healthcare, telecommunications, and gaming, by providing industry-specific solutions and technologies like analytics, artificial intelligence, and serverless computing. It was founded in 2006 and is based in Duvall, Washington.
Loading...
ESPs containing Amazon Web Services
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The generative AI — large language model (LLM) developers market offers foundation models and APIs that enable enterprises to build natural language processing applications for a number of functions. These include content creation, summarization, classification, chat, sentiment analysis, and more. Enterprises can fine-tune and customize these large-scale language models — which are pre-trained on …
Amazon Web Services named as Leader among 15 other companies, including Google, IBM, and OpenAI.
Loading...
Research containing Amazon Web Services
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Amazon Web Services in 13 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Sep 13, 2024.
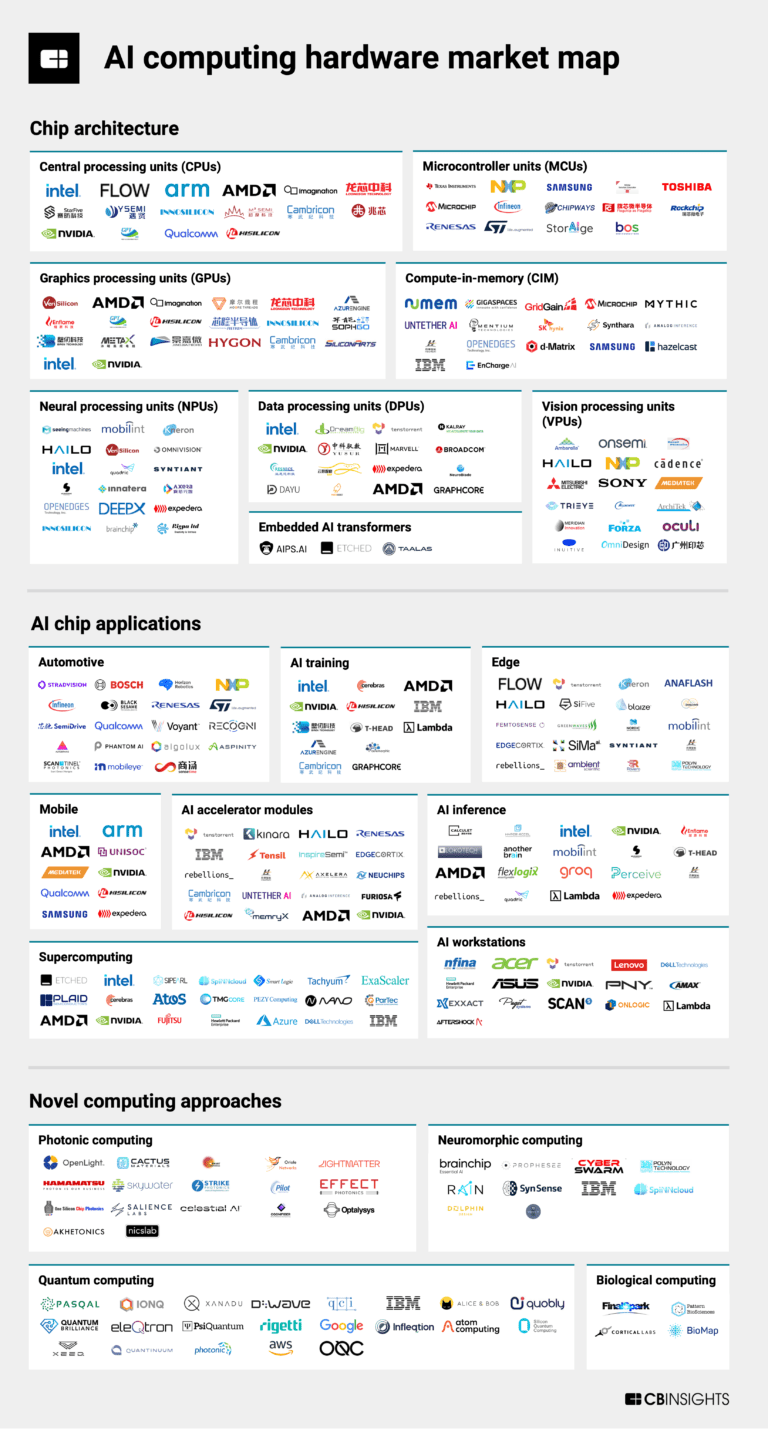
Sep 13, 2024
The AI computing hardware market map

Jan 11, 2024
The generative AI in healthcare market mapExpert Collections containing Amazon Web Services
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Amazon Web Services is included in 2 Expert Collections, including Conference Exhibitors.
Conference Exhibitors
5,302 items
ITC Vegas 2024 - Exhibitors and Sponsors
627 items
As of 9/9/24. Company list source: ITC Vegas. Check ITC Vegas' website for any updates: https://events.clarionevents.com/InsureTech2024/Public/EventMap.aspx?shMode=E&ID=84001
Latest Amazon Web Services News
Sep 20, 2024
| Amazon Web Services Published: Amazon OpenSearch Service is a managed service that makes it easy to deploy, operate, and scale OpenSearch domains in AWS to perform interactive log analytics, real-time application monitoring, website search, and more. Understanding OpenSearch service spend per domain is crucial for effective cost management, optimization, and informed decision-making. Amazon OpenSearch Service Pricing is based on three dimensions: instances, storage, and data transfer. Storage pricing depends on the chosen storage type and also the storage tier. Visibility into domain-level charges enables accurate budgeting, efficient resource allocation, fair cost attribution across projects, and overall cost transparency. In this post, we show you how to view the OpenSearch Service domain-level cost using AWS Cost Explorer. For example, the account in the following screenshot has five OpenSearch Service domains deployed. Using AWS Cost Explorer, you can see the cost at the service level by default but not at an individual domain level. However, users can still breakdown the cost using a dimension like Usage type. The simplest approach to gain domain level visibility is by enabling resource-level data in AWS Cost Explorer. There are no additional charges for enabling resource-level data at daily granularity in AWS Cost Explorer. If you need domain-level cost data beyond 14 days then either you can setup a Data Export/CUR or you can use user-defined cost allocation tags . User-defined cost allocation tags offer benefits such as cost categorization and cost allocation to categorize and group your AWS costs across cost centers and based on criteria that are meaningful to your organization, such as projects, departments, environments, or applications. This provides better visibility and granularity into your cost breakdown compared to just looking at resource-level costs. Overview This post demonstrates how to use user-defined cost allocation tags attached to a cluster using these high-level steps: Add a user-defined cost allocation tag to an OpenSearch Service domain Activate the user-defined cost allocation tag Analyze OpenSearch Service domain costs using AWS Cost Explorer and tags Prerequisites 1. Add a user-defined cost allocation tag to an OpenSearch Service domain The user-defined cost allocation tags are key-value pairs and user will need to define both a key and a value to an OpenSearch Service domain using one of the following methods: AWS Management Console AWS CLI To add a user-defined cost allocation tag using the AWS CLI, you can use the aws opensearch add-tags command to add tags to an OpenSearch Service domain. The command requires the domain Amazon Resource Name (ARN) and a list of tags to be added. Use the following syntax. add-tags --arn=<domain_arn> --tag-list Key=<key>,Value=<value> Example: Amazon OpenSearch Service configuration API You can use the Amazon OpenSearch Service configuration API to create, configure, and manage OpenSearch Service domains. Use the following AddTags command to tag an OpenSearch Service domain. POST /2021-01-01/tags HTTP/1.1Content-type: application/json{ "ARN": "arn:aws:es:us-east-1:123456789123:domain/opensearchtestdomain", "TagList": [ { "Key": "opensearchdomain", "Value": "opensearchtestdomain" } ]} AWS SDK You can programmatically add tags to an OpenSearch Service domain using the AWS OpenSearch SDK. The SDK provides methods to interact with Amazon OpenSearch Service API and manage tags. For example, Python client can use the client.add_tags command to tag a domain. You must provide values for domain_arn, tag_key, and tag_value. import boto3client = boto3.client('opensearch')response = client.add_tags ( ARN = ‘arn:aws:es:us-east-1:123456789123:domain/opensearchtestdomain’, TagList=[ { ‘Key’: ‘opensearchdomain’, ‘Value’: ‘opensearchtestdomain’ } ]) AWS CloudFormation or Terraform When provisioning an OpenSearch Service domain using CloudFormation or Terraform, you can define the tags as part of the resource configuration by using AWS::OpenSearchService::Domain Tag . Resources OpenSearchDomain: Type: AWS::OpenSearchService::DomainProperties DomainName: arn:aws:es:us-east-1:123456789123:domain/opensearchtestdomainTags - Key: opensearchdomain - Value: opensearchtestdomain After applying a user-defined tag to the OpenSearch Service domain, use the following AWS CLI command to verify that the tag has been applied. aws opensearch list-tags –arn <ARN> Example: Troubleshooting The add-tags command can fail in the following scenarios, so make sure all the values are entered correctly: Invalid resource ARN – The command will fail if the provided ARN for the OpenSearch Service domain is invalid or does not exist. Insufficient permissions – Verify that the IAM user or role you’re using to run the OpenSearch Service commands has the necessary permissions to access the OpenSearch Service domain and perform the desired actions, such as adding tags. Exceeded tag limit – The OpenSearch Service domain has limit of up to 10 tags , so if the number of tags you are trying to add exceeds this limit, the command will fail. For ease of use and best results, use the Tag Editor to create and apply user-defined tags. The Tag Editor provides a central, unified way to create and manage your user-defined tags. For more information, refer to Working with Tag Editor in the AWS Resource Groups User Guide . 2. Activate the user-defined cost allocation tag User-defined cost allocation tags are tags that you define, create, and apply to resources, and it may take up to 24 hours for the tag keys to appear on your cost allocation tags page for activation in the Billing and Cost Management console. After you select your tags for activation, it can take an additional 24 hours for tags to activate and be available for use in Cost Explorer. Use the following steps to activate the user-defined cost allocation tags you created in previous steps. As shown in the following screenshot, on the Billing and Cost Management dashboard, in the navigation pane, select Cost Allocation Tags. To activate the tag, under User-defined cost allocation tags, enter opensearchdomain to search for your tag name, select it, and choose Activate. This confirms that Cost Explorer and your AWS Cost and Usage Reports (CUR) will include these tags. In general, cost allocation tags cannot be deleted and can only be deactivated. However, you can exclude the tag that you do not want in the CUR report or in AWS Cost Explorer and only include tags that are needed. 3. Analyze OpenSearch Service domain cost using AWS Cost Explorer and tags AWS Cost Explorer only displays tags starting from the date when you have enabled user-defined cost allocation tags and not from when the resource was tagged. Therefore, even if your resources had tags for a long time, AWS Cost Explorer will show “No tag key” for all of the previous days until the date when tag was enabled, but users can request to backfill tags . To analyze OpenSearch Service domain costs using AWS Cost Explorer and tags, follow these steps: On the Billing and Cost Management console, in the navigation pane, under Cost analysis, choose Cost Explorer. In the Report parameters help panel on the right, under Group by, for Dimension, select Tag. Under Tag, choose the opensearchtestdomain tag key that you created. Under Applied filters, choose OpenSearch Service. The following screenshot shows the CUR dashboard. Costs There is no additional fee or charge for using the user-defined cost allocation tags in AWS Cost Explorer. However, an excessive number of tags can increase the size of your CUR file. Your CUR file contains your usage and cost data, including tags you apply, so more tags mean more data in the file. CUR data is stored in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), so larger CUR file could increase storage cost. The best practice is to be selective about which tags you enable and how many you use. Start with tags that provide the most value for attributes such as cost allocation and analytics. Monitor your CUR file size over time and add and remove tags thoughtfully. Conclusion This post outlines a solution for AWS customers to gain visibility into their OpenSearch Service workload costs on a per-domain basis using AWS Cost Explorer and user-defined cost allocation tags. This approach enables greater cost transparency and control, making it easier to allocate costs accurately and make informed decisions about Amazon OpenSearch service workload usage. The process involves adding a cost allocation tag to each OpenSearch Service domain, activating the user-defined tag, and then analyzing the costs in AWS Cost Explorer based on the tag. By implementing this solution, customers can obtain granular insights into OpenSearch Service workload costs at the domain level, facilitating precise cost attribution and better alignment of costs with business requirements. For more resources, refer to the following: About the Authors Nikhil Agarwal is a Sr. Technical Manager with Amazon Web Services. He is passionate about helping customers achieve operational excellence in their cloud journey and actively working on technical solutions. He is an artificial intelligence (AI/ML) and analytics enthusiastic, he deep dives into customer’s ML and OpenSearch service specific use cases. Outside of work, he enjoys traveling with family and exploring different gadgets. Rick Balwani is an Enterprise Support Manager responsible for leading a team of Technical Account Mangers (TAMs) supporting AWS independent software vendor (ISV) customers. He works to ensure customers are successful on AWS and can build cutting-edge solutions. Rick has a background in DevOps and system engineering. Ashwin Barve is a Sr. Technical Manager with Amazon Web Services. In his role, Ashwin leverages his experience to help customers align their workloads with AWS best practices and optimize resources for maximum cost savings. Ashwin is dedicated to assisting customers through every phase of their cloud adoption, from accelerating migrations to modernizing workloads.
Amazon Web Services Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Amazon Web Services founded?
Amazon Web Services was founded in 2006.
Where is Amazon Web Services's headquarters?
Amazon Web Services's headquarters is located at 410 Terry Avenue North, Duvall.
Who are Amazon Web Services's competitors?
Competitors of Amazon Web Services include Rhino.ai, Cubbit, Expanso, Skytap, Genezio and 7 more.
Loading...
Compare Amazon Web Services to Competitors

Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service created by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers.

Google Cloud Platform specializes in providing cloud computing services. The company offers a suite of cloud solutions including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, data analytics, computing, storage, and networking capabilities designed to help businesses scale and innovate. Google Cloud Platform caters to various sectors such as retail, financial services, healthcare, media and entertainment, telecommunications, gaming, manufacturing, supply chain and logistics, government, and education. It was founded in 2008 and is based in Mountain View, California.

Databricks is a data and AI company that specializes in unifying data, analytics, and artificial intelligence across various industries. The company offers a platform that facilitates data management, governance, real-time analytics, and the building and deployment of machine learning and AI applications. Databricks serves sectors such as financial services, healthcare, public sector, retail, and manufacturing, among others. It was founded in 2013 and is based in San Francisco, California.
Alibaba Cloud specializes in cloud computing and data management services within the technology sector. The company offers scalable, secure, and reliable cloud services, including elastic computing, data storage, and database management solutions. Alibaba Cloud caters to a diverse range of customers, including businesses of various sizes, financial institutions, and government entities. It was founded in 2009 and is based in Hangzhou, Zhejiang . Alibaba Cloud operates as a subsidiary of Alibaba.com.

Cloudera operates as a company focused on data management and analytics in the technology sector. It offers a hybrid data platform that enables secure data management and portable cloud-native data analytics, allowing businesses to transform complex data into clear and actionable insights. It primarily serves sectors such as financial services, telecommunications, public sector, retail, insurance, manufacturing, healthcare, and education. The company was founded in 2008 and is based in Santa Clara, California.
DataRobot specializes in artificial intelligence, offering an open, end-to-end AI lifecycle platform within the technology sector. The company provides solutions for scaling AI applications, monitoring and governing AI models, and driving business value through predictive and generative AI. DataRobot serves various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and financial services, with its AI platform. It was founded in 2012 and is based in Boston, Massachusetts.
Loading...