Emerging technologies like digital twins and AI route optimization are making it easier to communicate and plan across a traditionally fragmented industry. We look at how Google is bringing new cloud offerings that enable more efficient and sustainable supply chains.
Many of today’s supply chain issues are exacerbated by the industry’s high fragmentation and slow digitization.
This has created opportunities for tech companies that are able to increase visibility and improve efficiencies, particularly using AI and ML (machine learning). In 2023, an estimated 60% of global organizations plan to invest in digital supply chain technologies.
Big tech players’ access to a wide range of data — from weather patterns to e-commerce transactions — and their proprietary AI/ML systems make them uniquely positioned to serve the supply chain industry from first mile to last.
Google in particular is relying on its strength in cloud computing and its access to real-time logistics data via Google Maps to deliver new supply chain tools. This could help Google upsell existing Cloud clients on a wider range of services and ultimately take market share from more dominant cloud providers like AWS.
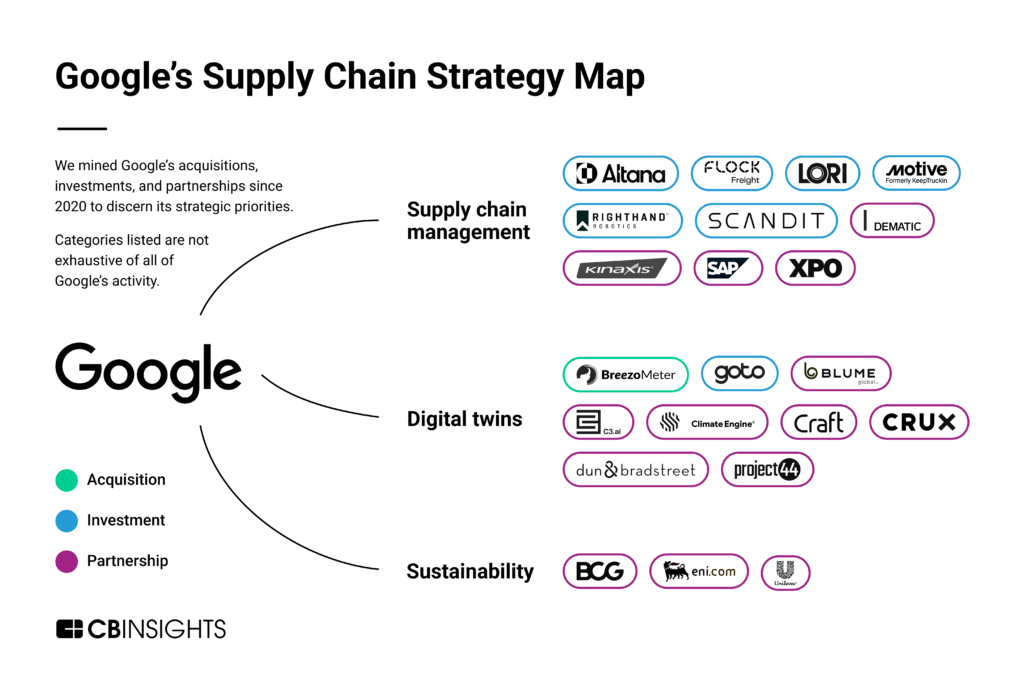
In this report, we break down Google’s strategy in supply chain across 3 key takeaways:
-
- Google is leveraging its own AI/ML capabilities for supply chain offerings. The search giant is using existing consumer products like Google Maps to release software that helps supply chain managers deploy fleets more quickly and plan routes more efficiently.
- Google is modernizing the supply chain with digital twins. Google is an early mover in simulating supply chains via digital twins to more accurately track and predict logistics issues.
- Google is investing in supply chain sustainability. Through multiple areas of its business, Google is creating products and inking partnerships that promote supply chain sustainability by tracking resources like raw materials and fuel.
Google is leveraging its own AI/ML capabilities for supply chain offerings
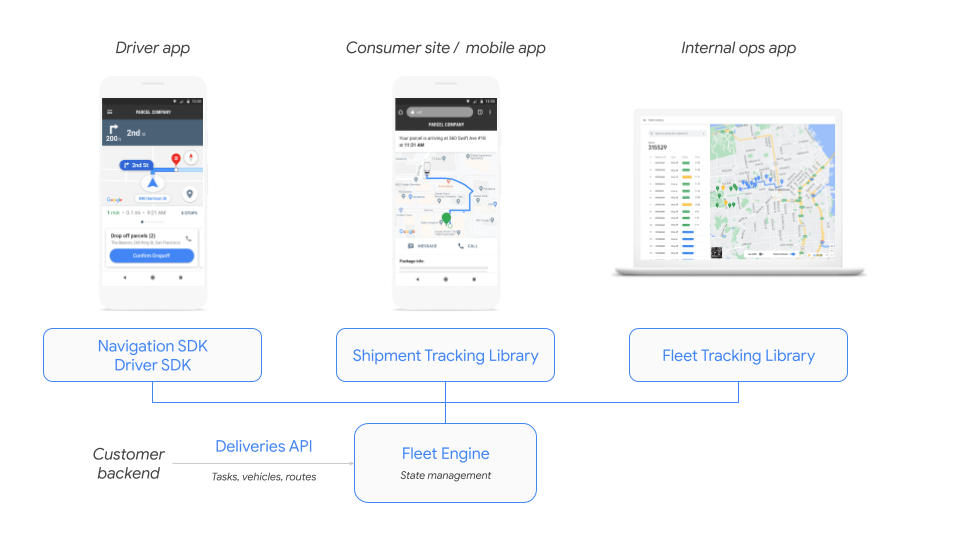
Google has released numerous software applications for supply chain managers recently that piggyback on its existing AI/ML capabilities. These include:
- Optimization AI, released in 2022, is a cloud fleet routing API for first- and last-mile delivery fleets. It helps supply chain managers optimize fleet planning for fuel and time efficiency by solving small-route planning problems like traffic and reducing delivery estimates.
- Last Mile Fleet Solution, also launched in 2022, syncs with the API to give employees a user-friendly Google Maps interface to help guide speedy deliveries.
Currently, these products can be used in addition to a supplier’s existing technologies or as an end-to-end solution. This go-to-market strategy is especially important given that many customers will need time to migrate over from legacy systems.
Google’s Last Mile Fleet Solution. Source: Google
Additionally, Google has partnered with logistics leader XPO to support its customers with cloud-optimized loads and routes. Google has also paired up with supply chain automation provider Dematic to offer AI/ML technologies for e-commerce and omnichannel fulfillment.
Historic inflation, rising fuel costs, and labor shortages have made the supply chain increasingly expensive. To mitigate these forces and increase profitability, companies have been investing in owning more of their supply chain.
Google Cloud already supports large players in a variety of industries from retail to healthcare. As Google Cloud covers more ground with its supply chain features, it’s aiming to embed itself in these clients’ expanding supply chain ambitions.
Incorporating logistics data from Google Maps also helps differentiate Google’s supply chain offering from Amazon’s long-standing third-party logistics (3PL) business.
Google is modernizing the supply chain with digital twins
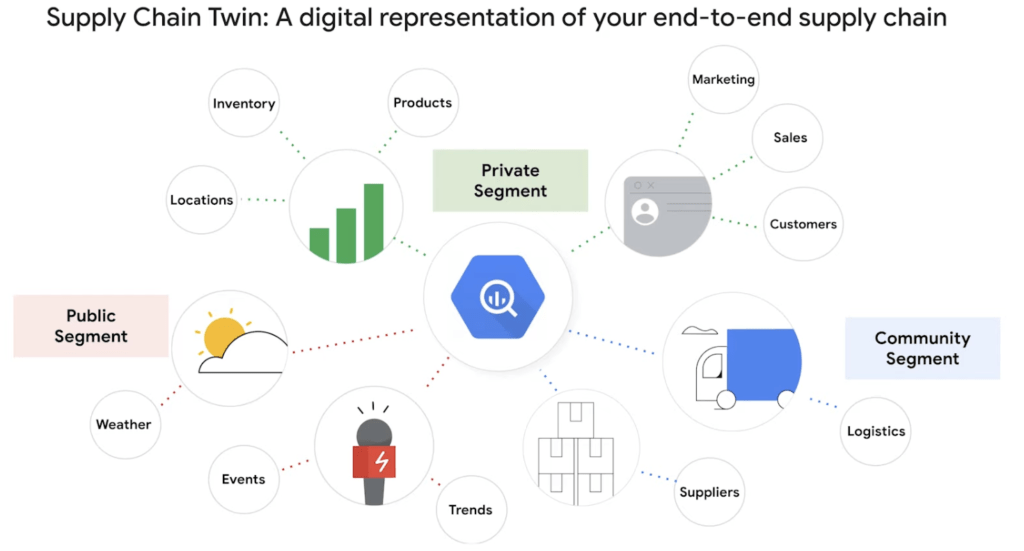
Digital twins are virtual simulations of real-world physical objects and systems that can model potential scenarios.
In supply chain planning, they can combine data from various sources — like a user’s supply chain stack, weather, and traffic patterns — to improve visibility, predict environmental patterns, optimize inventory, and identify process improvements.
Big tech players with advanced cloud platforms and computing capabilities have been early leaders in developing these solutions for supply chains. In Q3’21, Google announced its Supply Chain Twin, a digital twin creator within the Google Cloud ecosystem.
Armed with this tool, supply chain leaders can make strategic decisions to create more efficient operations or reduce delays when unexpected logistics issues occur. Google customers have seen up to a 95% reduction in analytics processing time using Supply Chain Twin.
Google has augmented its digital twin offering through acquisitions and partnerships. For instance:
- Google’s 2022 acquisition of environmental data provider BreezoMeter allows it to more accurately model local environmental conditions throughout the supply chain.
- Google has partnered with C3.ai to integrate elements of the enterprise AI firm’s product suite into Google Cloud. The combination is helping supply chain managers more accurately model potential risks to their drivers, fleets, and cargo.
Source: Google
Similar to Google’s other supply chain offerings, Supply Chain Twin is another way the big tech company has extended its cloud computing abilities to drive additional revenue.
The logistics space is highly fragmented, which could make it challenging to build out digital twins for entire networks. However, Google’s existing cloud product and customer breadth, as well as its external acquisitions and partnerships, could help it put together more pieces of the supply chain puzzle.
Google is investing in supply chain sustainability
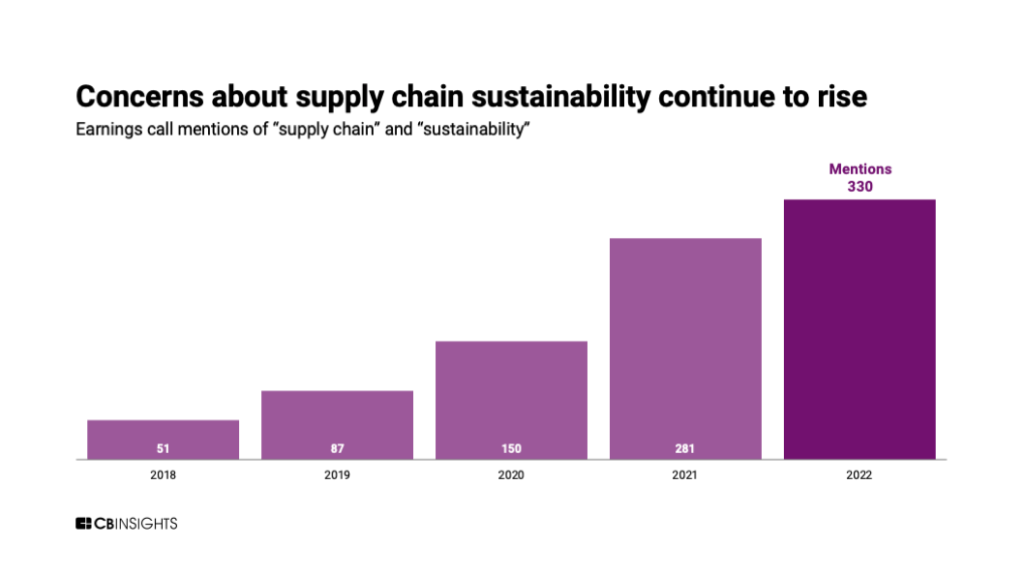
In many industries, supply chains account for over 80% of greenhouse gas emissions.
Across Google’s efforts in supply chain management, the tech giant has sought to help clients reduce emissions by building more sustainable and resilient supply chains. Google itself currently operates carbon-neutral with the goal of running its data centers using carbon-free energy sources by 2030.
Google’s cloud-based offerings like Supply Chain Twin enable supply chain leaders to receive more accurate analysis to determine where processes can be improved. For instance, fleets can be loaded more effectively, be tracked more accurately, and drive more fuel-efficient routes. Delivery giant UPS, for instance, has used Google Cloud’s analytics platform to reduce fuel consumption by 10M gallons annually.
Google’s data can be implemented even earlier in the supply chain to meet sustainability goals. For instance, Unilever has used Google Earth’s satellite imagery and AI to detect deforestation in its supply chain. Google also partnered with Boston Consulting Group and energy provider Eni in 2021 to found Open-es, a platform to help companies measure the environmental impact of their supply chains and collaborate on the energy transition.
Going beyond data analytics, Google has also been experimenting with delivery vehicles. As of 2022, its parent company Alphabet has completed over 250K last-mile deliveries with its drone division Wing.
As regulators and consumers warm up to the idea of using drones for delivery, it’s possible that Google may offer a full end-to-end supply chain solution that incorporates these vehicles — which release 84% fewer emissions and use 94% less energy per package than diesel trucks.
If you aren’t already a client, sign up for a free trial to learn more about our platform.