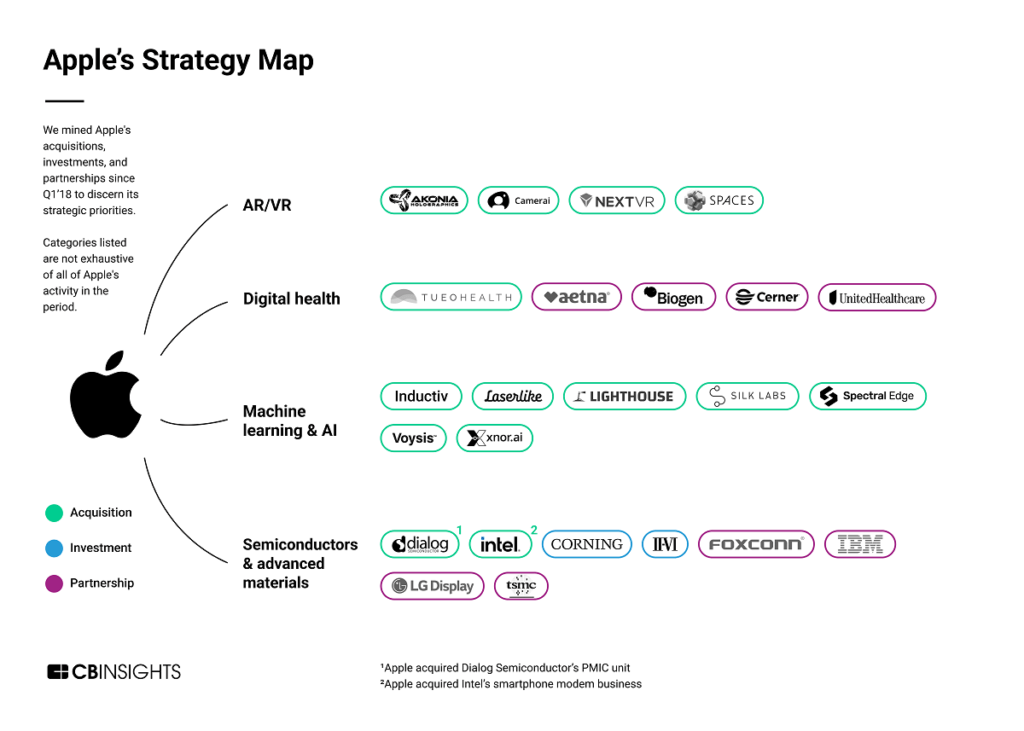
We mined Apple's acquisitions, investments, and partnerships to discern the company's emerging strategic priorities.
Apple is looking for the next big thing.
As the world’s most valuable company, with a $2T+ market cap and over $100B in annual profit, Apple has long been known for its cell phones, laptops, tablets, and watches. Today, the company is investing aggressively in high-tech areas like AR/VR, AI, and semiconductors to lay the groundwork for products and features that affect health & wellness, mobility, digital connections, and more.
<![endif]-->
<script charset="utf-8" type="text/javascript" src=https://www.cbinsights.com/research/apple-strategy-map-investments-partnerships-acquisitions/"//js.hsforms.net/forms/v2.js">
<script>
hbspt.forms.create({
onFormReady: function ($form) {
window.ClearbitForHubspot.addForm($form);
},
region: "na1",
portalId: "763793",
formId: "2465d613-bb70-4d69-8785-cb3805b1f24e"
});
</script></div></div></div>"}" data-sheets-userformat="{"2":2561,"3":{"1":0},"12":0,"14":{"1":2,"2":0}}"> Download our full report to find out the top trends poised to reshape industries in 2022.download the 12 Tech Trends To Watch Closely In 2022 report
Although Apple is famously secretive, its acquisitions, partnerships, and investment activity provide a window into where it’s headed next. The company has acquired more than 25 companies since 2018, from edge-based AI startup Xnor.ai to VR streaming platform NextVR. Apple has also committed $430B for new investments and 20,000 new jobs in the US over 5 years — in addition to further investments in Europe and India — across silicon engineering, AI, and 5G tech.
Using CB Insights data, we uncovered 4 of Apple’s emerging strategic priorities highlighted by its recent acquisitions, investments, and partnerships. We then categorized companies by their business relationships with Apple across these priorities.
- AR/VR
- Digital health
- Machine learning & AI
- Semiconductors & advanced materials
These designations are not exhaustive of Apple’s investment and partnership activity in the analyzed period.
AR/VR
Apple started investigating augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) applications over a decade ago, as evidenced by its patent activity. For example, its ARKit framework (launched in 2017) — which enables developers to build AR experiences into their apps — is now used in over 14,000 apps with over 13M total downloads.
In recent years, companies in the AR/VR space have become serious M&A targets for Apple, coinciding with rumors about its internal development of a mixed reality headset that is expected to release in 2023 (eventually followed by a sleeker pair of glasses).
In 2018, Apple acquired 2 companies in the space: Camerai, an Israel-based computer vision and AR tech company, and Akonia Holographics, an AR optics developer. These purchases helped grow Apple’s patent portfolio and talent, setting the foundation for its future AR products.
Then in 2020, Apple acquired two VR companies. First was NextVR for a reported $100M, which developed solutions for the capture and delivery of sports and entertainment virtual reality content. A few months later, Apple purchased Spaces, which created location-based and themed virtual environments.
While Apple has not been explicit about its metaverse ambitions like fellow big tech giant Meta, its continued investment in AR/VR sets it up for more immersive digital environments of the future — and the hardware they may need.
Digital health
Apple is continuing to cement its focus in health as part of a wider strategic priority, as we’ve previously examined here and here. Apple is also working with companies, universities, app developers, and others to move this priority forward.
Central to this strategy are Apple devices, such as the Apple Watch and iPhone, which enable users to track, aggregate, and share their health data.
The company’s research teams are actively exploring new health indicators the Apple Watch could help monitor. Last year, Apple announced a collaboration with Biogen IDEC to investigate how the device can detect declines in cognitive health. Apple has also teamed up with several university and government partners — such as the NIH, the White House, Harvard, UCLA, and the University of Michigan — to conduct studies that use Apple devices to address issues ranging from Covid-19 to noise exposure to women’s health.
Meanwhile, Apple has landed agreements with major health plans like UnitedHealthcare and Aetna to offer subsidized Apple Watches and other wellness services to members.
In 2019, the company purchased Tueo Health, which developed a system to help parents monitor asthma symptoms in sleeping children. This acquisition is further indication of Apple’s intention to engage consumers on health & wellness.
Machine learning & AI
Apple has aggressively acquired companies across the machine learning (a type of AI that leverages past data to understand future scenarios) and AI space — outpacing fellow tech giants like Google and Microsoft — to shore up its AI efforts.
Apple’s AI acquisition spree has been essential to the development of new iPhone features. Many of its purchases are positioned to enhance its virtual assistant, Siri, but they also have applications across many other parts of its software.
For example, Apple acquired in 2019 and 2020:
- Laserlike, an ML platform that could better personalize Siri, news feeds, and video apps for individual users.
- Voysis, to improve Siri’s language understanding.
- Inductiv, which developed an AI platform to automatically identify and correct errors in datasets, helping software to improve with less human intervention.
- Spectral Edge, a company with infrared tech that could enhance iPhone photos.
In January 2020, Apple also acquired Xnor.ai for a reported $200M, which specialized in developing highly efficient ML models deployed at the edge. The edge computing startup could enhance a number of Apple’s device ML models, including those related to capturing and processing images, natural language processing, and object recognition.
Other AI acquisitions include Lighthouse AI, a developer of AI-powered home security cameras, and Silk Labs, which developed on-device ML software. These possibly point to Apple strengthening its smart speaker, the HomePod, with a focus on privacy by keeping data on the device.
Semiconductors & advanced materials
Apple is considered by some as the most advanced semiconductor design firm in the world. It’s also partnered with TSMC — the most advanced semiconductor production firm in the world — to produce chips. Semiconductor production is an extremely complex manufacturing process, making this partnership critical.
Apple’s design history started in 2008, when the company made the prescient purchase of PA Semi, a semiconductor design firm. Apple understood that if it wanted the best consumer experience possible, it needed to design its own chips, tailored to its own devices.
In the years since, Apple has remained aggressive in semiconductor design. The company purchased Intel‘s smartphone modem business in 2019 for $1B, giving it a significant patent portfolio and 2,200 former Intel employees. This followed the acquisition of Dialog Semiconductor‘s power management division in 2018 for $600M.
Apple has built out its semiconductor capabilities further with investments in critical suppliers, including Corning and II-VI. Corning is the manufacturer of Gorilla Glass, a durable glass used for iPhone screens. On top of the $450M it’s already given to Corning, Apple invested $45M in the company in 2021 — coinciding with the rise of bendable iPhone rumors, though no official purpose for the funding was given.
Meanwhile, Apple invested $410M in II-VI in 2021, building on its $390M investment in II-VI-owned Finisar in 2017. II-VI makes the optical technologies that power features like Face ID and Portrait mode, as well as the lasers used in Apple’s LiDAR Scanner, which is used to create AR experiences.
In addition to these investments, Apple has developed partnerships with leading firms such as Foxconn, one of its main partners in iPhone production, and LG Display, a producer of its OLED displays.
Other categories
Beyond these 4 strategic areas, Apple has made noteworthy acquisitions, investments, and partnerships across a number of other categories.
Autos
Rumors of an Apple car have existed since 2014, further materializing in 2018 when the company partnered with Volkswagen to turn some of the carmaker’s vans into autonomous employee shuttles.
Over the past few years, Apple has also filed a number of car patents. Using CB Insights patents search tool, we can see that the company is focusing on traditional car technologies, such as thermal management systems and vehicle seating.
Beyond patents, Apple has made one acquisition in the space, purchasing autonomous driving startup Drive.ai in 2019. Apple has also reportedly held talks with Hyundai, Toyota, and Porsche — focusing on car and battery production in the US with Hyundai and Toyota, and car production with Porsche.
DIGITAL MEDIA & Services
Apple has grown its services segment — which includes Apple Music, Apple TV+, cloud services, and others — to nearly $20B in quarterly revenue, with 825M paid subscriptions as of the second quarter.
Alongside this growth, Apple has made multiple acquisitions of digital media companies over the last 2 years, including Scout FM, Vilnyx, Primephonic, and AI Music. These purchases are aimed at enhancing its music and podcasting capabilities, while the Vilynx purchase — for a reported $50M — provides AI tools that help analyze and understand videos.
Apple’s 2018 acquisition of digital magazine service Texture laid the foundation for its subscription service Apple News+, launched in 2019.
More recently, Apple notably invested in independent music distribution platform UnitedMasters, participating in the company’s 2021 Series B alongside Alphabet and Andreessen Horowitz. The company also partnered with Verizon to offer the telecom’s Unlimited customers a free trial of Apple Music, and with Comcast on a cross-platform distribution deal for their streaming apps.
FinTech
Apple first released Apple Pay — a digital wallet and mobile payment system — in 2014. Since then, Apple has continued to invest in payments and beyond.
In July 2020, the company acquired Mobeewave, which developed a solution to turn any NFC phone into a mobile payment terminal. Most recently, Apple purchased UK-based fintech Credit Kudos, which uses consumer banking data for better informed credit checks.
Apple has also developed partnerships to grow its services, including with PayHawk and Isracard to expand Apple Pay, and with Goldman Sachs to launch the Apple credit card.
If you aren’t already a client, sign up for a free trial to learn more about our platform.