
Neo4j
Founded Year
2007Stage
Series F - II | AliveTotal Raised
$581.1MValuation
$0000Last Raised
$66M | 3 yrs agoMosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
-64 points in the past 30 days
About Neo4j
Neo4j specializes in graph databases and analytics. The company offers a range of products and services including a graph database management system, graph data science tools, and professional services for data analysis and modeling. Its primary customers are organizations across various sectors looking to find hidden relationships and patterns in large data sets. Neo4j was formerly known as Neo Technology. It was founded in 2007 and is based in San Mateo, California.
Loading...
ESPs containing Neo4j
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The NoSQL database market revolves around the development, provision, and adoption of non-relational database management systems. NoSQL databases are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data, offering scalability, high performance, and flexibility compared to traditional relational databases. The market encompasses a variety of NoSQL database technologies, including…
Neo4j named as Outperformer among 15 other companies, including Microsoft Azure, Oracle, and Cloudera.
Loading...
Expert Collections containing Neo4j
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Neo4j is included in 2 Expert Collections, including Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups.
Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups
1,244 items
Tech IPO Pipeline
825 items
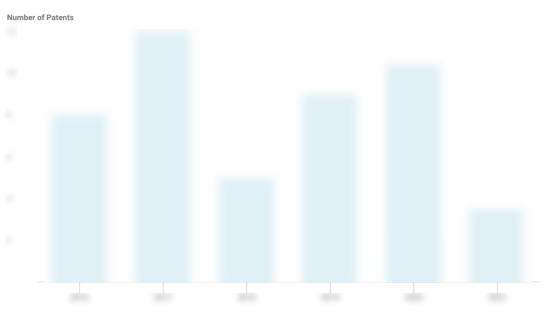
Neo4j Patents
Neo4j has filed 19 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- free database management systems
- database management systems
- data management
Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1/6/2021 | 9/10/2024 | Grant |
Application Date | 1/6/2021 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 9/10/2024 |
Title | |
Related Topics | |
Status | Grant |
Latest Neo4j News
Sep 13, 2024
Techgoondu Last updated: September 13, 2024 at 6:18 PM Kristen Pimpini, vice-president and general manager for Asia-Pacific at Neo4j. PHOTO: Neo4j At a time when AI is often operating in a “black box” and its outputs are unquestionably accepted , a relatively nascent form of database technology may help untangle how it arrives at a result, say its proponents. Graph databases focus on the nodes and relationships in a sea of data to reveal connections and insights not obvious with traditional databases. By revealing such connections, graph databases can help make AI applications more accurate, explainable and transparent, says Kristen Pimpini, vice-president and general manager for Asia-Pacific at Neo4j. For example generative AI (GenAI) chatbots can be more precise and detailed with training that taps on a knowledge graph of an organisation’s private data, he explains. Neo4j’s graph technologies have been widely deployed for a while, for example, by banks to help identify relationships between various data points and identify possible fraud. Now, graph technologies could also enhance AI. One way to do this is by presenting context, says Pimpini, in this month’s Q&A. “It helps to analyse data, spot patterns, and uncover misinformation.” NOTE: Responses have been edited for clarity and style. Q: We’ve had graph analytics and machine learning for a while now. What do the latest developments in AI bring to the table that wasn’t there before? A: GenAI is the new best friend of graph analytics and machine learning. Combining GenAI models such as large language models (LLMs) with graph databases results in AI applications that are more accurate, explainable, and transparent. A frustrating challenge facing companies right now is AI chatbots that don’t provide detailed and precise responses. This is where a machine-learning approach called RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) comes into play. In contrast to LLMs that are trained on publicly available data, RAG taps into a Neo4j knowledge graph composed of your own private data to give LLMs more context, so the answers are improved and more personalised. Furthermore, integrating Neo4j’s graph database with LLMs allows users to interact with knowledge graphs using natural language, making these tools accessible even to non-technical users. What used to be messy and unstructured data is now being transformed into knowledge graphs, that lead to deeper insights. Neo4j’s graph algorithms and data science tools also enable advanced analytics and machine learning on graph data structures. This allows organisations to use the predictive power of graphs to identify relationships and network patterns that can tackle complex challenges such as fraud detection, recommendation systems, and patient care management. Q: When it comes to fraud, are people justifiably worried about impersonation through AI, such as the recent case in Hong Kong where an executive was fooled into transferring millions to fraudsters because he thought he had a video call from his CFO? A: With AI advancements, deep fakes and fraud are on the rise, and it’s no surprise people are worried. Globally, fraud losses are expected to hit a staggering US$95.9 billion by 2027, and AI plays a big part in that. In Singapore, deep fake cases jumped tenfold this year. The underlying problem is that deep fake tech is evolving so quickly that fraud-detection systems struggle to keep up. Here’s where knowledge graphs shine through. By connecting data points to spot hidden patterns and anomalies, businesses can improve their fraud predictions. Even a small boost in fraud prediction accuracy can save companies millions. For example, Neo4j teamed up with BNP Paribas Personal Finance to build a new fraud detection model. By switching from a relational to a graph database, they could spot loopholes between credit applications that fraudsters exploit, making real-time payments more secure. Such efforts resulted in a 20 per cent drop in fraud, enabling automated fraud detection that approves or rejects applications in less than two seconds. Q: Would your AI tools that help deter fraud today be able to defend against more advanced fraud attempts, say, through a fake voice or video call? A: Traditional fraud detection tools just don’t cut it like they used to and prove to be a challenge in targeting today’s more sophisticated fraudsters. These tools often miss connections between real-world entities and rely too much on historical data, making it tough to catch real-time fraud, especially when new behaviours pop up that weren’t in the old data. While Neo4j isn’t specifically built to combat fraud, our graph technology is great at helping organisations spot and predict fraud by analysing connections between data points with greater speed and flexibility. Companies get a much clearer picture of potential threats to link fraudulent activities more easily and accurately in real time. Graph databases can also store complex networks of transactions, accounts, and people, making it easier to detect perceived threats as they happen. A useful example is the Panama Papers investigation . The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) used Neo4j’s graph database to untangle complex networks of offshore accounts, exposing the key people behind companies hiding money in tax havens – including 140 politicians from over 50 countries. Q: Seeing is no longer believing, as the saying now goes. Do you think AI will make a difference in a “post-truth” world where people already believe what they want to believe? A: AI is being increasingly used to spread misinformation and create deepfakes, making it harder to tell what’s real and what’s not, and potentially manipulating public opinion. It is a wake-up call for governments around the world to prioritise effective AI regulations. How AI shapes our post-truth world really depends on how ethically and responsibly we develop and use it. If done right, AI could be instrumental in restoring trust. Graph technology promotes the evolution of AI by empowering the development of sophisticated AI applications by presenting context. It helps to analyse data, spot patterns, and uncover misinformation. An example of this is the work Neo4j is doing with Syracuse University on election misinformation . Neo4j’s graph technology is helping to reveal hidden connections and interactions in a complicated network of social media content, identifying bad actors within a firehose of misinformation coming at voters ahead of the United States 2024 elections. You Might Also Like
Neo4j Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Neo4j founded?
Neo4j was founded in 2007.
Where is Neo4j's headquarters?
Neo4j's headquarters is located at 111 East 5th Avenue, San Mateo.
What is Neo4j's latest funding round?
Neo4j's latest funding round is Series F - II.
How much did Neo4j raise?
Neo4j raised a total of $581.1M.
Who are the investors of Neo4j?
Investors of Neo4j include One Peak Partners, Alanda Capital Management, Inovia Capital, Creandum, Heartcore Capital and 16 more.
Who are Neo4j's competitors?
Competitors of Neo4j include TigerGraph, Katana Graph, Ontotext, Slingshot Simulations, MarkLogic and 7 more.
Loading...
Compare Neo4j to Competitors
TigerGraph is a company focused on providing advanced analytics and machine learning on connected data through its graph database technology. The company offers a distributed native graph database platform that supports a range of applications, including fraud detection, anti-money laundering, and recommendation systems, among others. TigerGraph's solutions cater to various industries, including financial services, healthcare, and supply chain management. TigerGraph was formerly known as GraphSQL. It was founded in 2012 and is based in Redwood City, California.
DGraph specializes in providing an open source, AI-ready graph database designed for various industries. The company offers a scalable and high-performance database solution that supports real-time queries and distributed applications. DGraph's database is suitable for a range of use cases including knowledge graphs, recommendation systems, master data management, customer 360 views, and fraud detection. It was founded in 2016 and is based in Palo Alto, California.
Katana Graph is a company focused on data intelligence, operating within the technology and artificial intelligence sectors. The company offers a graph intelligence platform that uses advanced algorithms and neural network architecture to provide insights from large data sets, with applications in areas such as fraud detection, identity management, and drug discovery. Katana Graph primarily serves sectors such as financial services, health and life sciences, and security. It was founded in 2020 and is based in Austin, Texas.
ArangoDB is a company that focuses on providing graph database solutions in the technology sector. The company offers a scalable graph database platform, ArangoGraph Insights Platform, that enables data analytics and uncovers insights in complex data architectures, suitable for use cases such as fraud detection, supply chain management, network analysis, and more. ArangoDB primarily serves industries such as financial services, healthcare, and telecommunications. It was founded in 2014 and is based in San Mateo, California.
Objectivity is a company that specializes in NoSQL and graph databases within the data management and analytics industry. The company's main offerings include enterprise database software platforms that power critical, operational data and sensor fusion systems, enabling real-time data and graph analytics. These services primarily cater to sectors such as government, manufacturing, healthcare, and telecommunications. It is based in Sunnyvale, California.
LARUS is a software house that specializes in the design and implementation of customized solutions for business-critical applications across various sectors. The company offers services such as consulting, coaching, and training in Agile and Lean methodologies, as well as developing technologies for data visualization, explainable AI, and data governance. LARUS primarily serves sectors that require advanced data analytics and decision-making support systems. It was founded in 2004 and is based in Venice, Italy.
Loading...