PayPal
Founded Year
1998Stage
PIPE - II | IPOTotal Raised
$203MMarket Cap
74.75BStock Price
77.57Revenue
$0000About PayPal
PayPal operates as a financial technology company. It specializes in digital payment solutions. The company offers a range of services including digital wallets, money management, peer-to-peer transfers, merchant payment processing, and credit products. PayPal caters to individual consumers, small businesses, and large enterprises with tailored payment and financial services. PayPal was formerly known as X.Com. It was founded in 1998 and is based in San Jose, California.
Loading...
ESPs containing PayPal
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The real-time payments (RTP) processing market provides infrastructure and technologies to facilitate instant and seamless electronic payments. This market offers solutions that enable the immediate transfer of funds between financial institutions or individuals, allowing for real-time settlement of transactions. Businesses can benefit from enhanced speed, efficiency, and convenience in their paym…
PayPal named as Leader among 15 other companies, including Mastercard, Visa, and Temenos.
PayPal's Products & Differentiators
PayPal
Millions of people trust PayPal to buy, sell, and send money—without sharing their financial information.
Loading...
Research containing PayPal
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned PayPal in 21 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Aug 14, 2024.

Aug 14, 2024
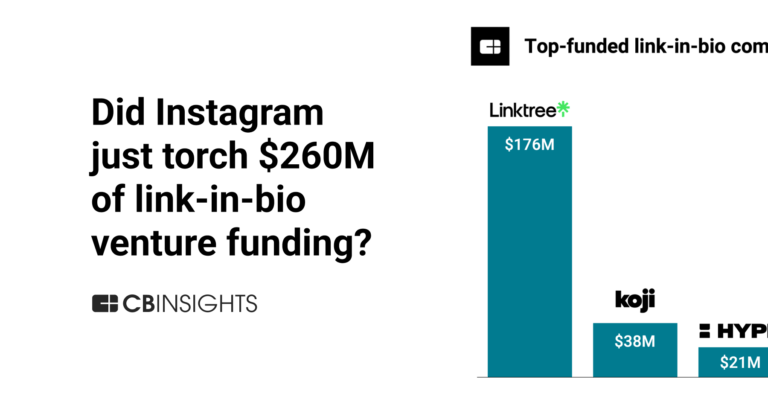
Crypto is showing signs of life in payments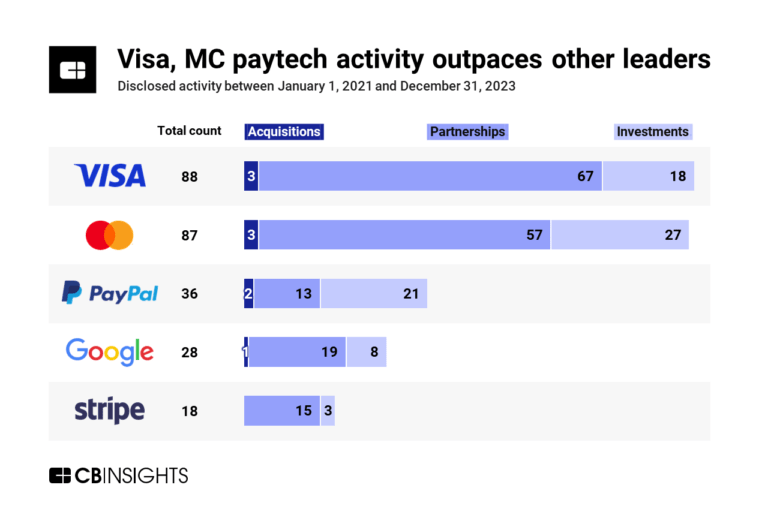
Jan 18, 2024 report
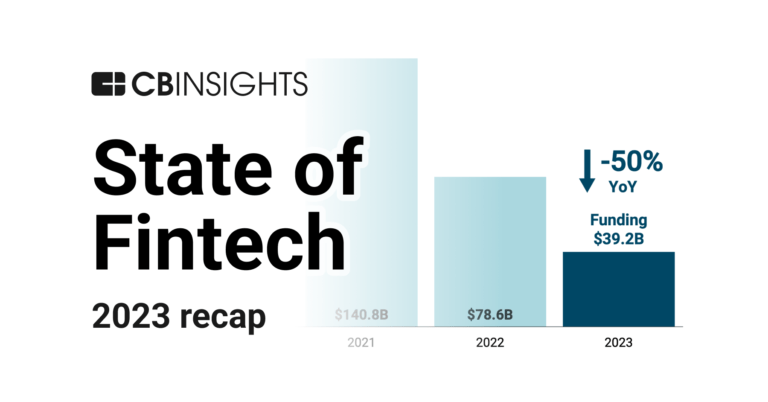
State of Fintech 2023 Report
Nov 9, 2023 team_blog
How can private equity buyers identify corporate spin-off/divestiture candidates?
Oct 10, 2023 report
The most active startup accelerators and where they’re investing
Expert Collections containing PayPal
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
PayPal is included in 8 Expert Collections, including Blockchain.
Blockchain
8,779 items
Companies in this collection build, apply, and analyze blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies for business or consumer use cases. Categories include blockchain infrastructure and development, crypto & DeFi, Web3, NFTs, gaming, supply chain, enterprise blockchain, and more.
Fortune 500 Investor list
590 items
This is a collection of investors named in the 2019 Fortune 500 list of companies. All CB Insights profiles for active investment arms of a Fortune 500 company are included.
SMB Fintech
1,586 items
Gig Economy Value Chain
155 items
Startups in this collection are leveraging technology to provide financial services and HR offerings to the gig economy industry
Payments
3,033 items
Companies in this collection provide technology that enables consumers and businesses to pay, collect, automate, and settle transfers of currency, both online and at the physical point-of-sale.
Conference Exhibitors
5,302 items
PayPal Patents
PayPal has filed 3147 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- payment systems
- payment service providers
- data management
Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1/28/2020 | 9/17/2024 | Google services, Transaction processing, Commerce websites, Databases, Biological databases | Grant |
Application Date | 1/28/2020 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 9/17/2024 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Google services, Transaction processing, Commerce websites, Databases, Biological databases |
Status | Grant |
Latest PayPal News
Sep 20, 2024
This iframe contains the logic required to handle Ajax powered Gravity Forms. As the financial world evolves, open banking and digital transformation bring new opportunities. This comes with several challenges for banks and fintechs. In today’s episode of the Tearsheet podcast, host Zack Miller sits down with Alessandro Hatami. He is the managing partner of Pacemakers. Today we discuss these seismic shifts in the fintech industry. Hatami has a unique background in fintech. It spans both innovative companies like PayPal and traditional institutions like Lloyds Bank. His background offers a compelling perspective on the future of financial services. “Financial services is the ideal digital product,” Hatami asserts. “because there isn’t a real tangible exchange,” he says. Yet, despite this potential, many institutions are struggling to embrace digital transformation. Hatami explains, “They have gone through an evolution. But they haven’t gone through a transformation.” The challenge facing the industry today lies in balancing adaptation with true transformation. from legacy systems to cultural barriers. Through Pacemakers, Hatami aims to bridge this gap. He wants to ease partnerships between established financial institutions and agile fintech innovators. Three Stages of Financial Services Innovation Hatami outlines a three-stage model of innovation in financial services: Adapting – Banks begin by adapting existing capabilities to digital platforms. Evolving – Institutions develop new digital-only services not possible in traditional branch settings. Transforming – The toughest stage is rethinking financial services with a customer-centric perspective. “What’s on the other side is a financial services proposition. It is not designed to sell a product to an individual. But it’s designed at understanding what the individual needs,” Hatami explains. Overcoming Challenges in Fintech Partnerships Successful collaborations between incumbents and fintech face several hurdles: Timing mismatches between fast-moving startups and slower corporate processes Difficulty in translating innovative propositions into terms that resonate with traditional banks Identifying the right internal champion with P&L responsibility Hatami advises, “You have to explain to the big company what you could do for them. But you have to explain to them in their terms.” Rise of Open Banking and “Banking as a Platform” The concept of open banking is transforming the consumption and delivery of financial services. Hatami predicts, “The future in banking will be. The banks will become the gatekeeper of my financial relationship. The bank may or may not deliver the services and products I receive. “Banking as a platform” is a major shift from the old model where banks made all their products themselves. Now, banks collaborate with others to offer a wider range of services. Role of AI in Reshaping Financial Services Artificial Intelligence presents enormous opportunities for the financial sector. Particularly in data processing and pattern recognition. AI will likely support, not replace, human interaction in customer service roles. “The way I think about AI is about it as an efficient, effective, interesting way of capturing data. Through the new visualization techniques. And also processing gigantic amounts of data,” Hatami explains. Cultural Transformation: From Product-Centric to Customer-Centric The biggest challenge is shifting from a product-centric to a customer-centric approach. This requires a cultural change. It needs banks to completely reorganize their operations. And change how they measure success. Hatami notes, “In a customer-centric world, banks must use customer segmentation for their profits and losses. Not just product-based metrics. This requires a complete transformation of how banks operate.” The Big Ideas Digital transformation in financial services is vital. “They have gone through an evolution. But they haven’t gone through a transformation,” Hatami observes. Banks must move beyond adapting existing services. They must reimagine their role in customers’ financial lives. Hatami highlights the importance of cultural alignment in partnerships. “You have to explain to the big company what you could do for them, but you have to explain to them in their terms,” he advises. Successful collaborations need mutual understanding and clear communication. Open Banking is the future of fintech. “The future in banking will be. The banks will become the gatekeeper of my financial relationship,” Hatami predicts. This shift will change the delivery of financial services. Hatami focuses on the role of AI in financial services. “The way I think about AI is as an efficient, effective, interesting way of capturing data,” Hatami explains. While AI offers significant opportunities, human interaction remains crucial in financial services. Hatami highlights the shift to customer-centric banking. “In a world where the customer is centric, they go through the segmentation P&L, not the product P&L,” he notes. This fundamental shift requires completely transforming how banks operate and measure success. Listen to the full episode
PayPal Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was PayPal founded?
PayPal was founded in 1998.
Where is PayPal's headquarters?
PayPal's headquarters is located at 2211 North First Street, San Jose.
What is PayPal's latest funding round?
PayPal's latest funding round is PIPE - II.
How much did PayPal raise?
PayPal raised a total of $203M.
Who are the investors of PayPal?
Investors of PayPal include Elliott Management, Third Point, eBay, ebank Financial Services, Bankinter and 28 more.
Who are PayPal's competitors?
Competitors of PayPal include TerraPay, Merchantrade, Stripe, FlexM, Worldpay and 7 more.
What products does PayPal offer?
PayPal's products include PayPal and 4 more.
Who are PayPal's customers?
Customers of PayPal include United Airlines.
Loading...
Compare PayPal to Competitors

Stripe operates as a technology company that specializes in online payment processing and financial infrastructure for Internet businesses. The company provides a suite of products that enable businesses to accept payments, manage billing and subscriptions, handle in-person transactions, and integrate various financial services into their operations. Its platform is designed to support startups, enterprises, and everything in between with scalable, API-driven solutions. Stripe was formerly known as DevPayments. It was founded in 2010 and is based in South San Francisco, California.

Worldpay provides electronic payment processing services to merchants and financial institutions. It offers merchant acquiring and payment processing services, such as authorization and settlement, customer service, chargeback and retrieval processing, and interchange management for national merchants, and regional and small-to-medium-sized businesses. The company was founded in 1993 and is based in London, United Kingdom.

PayU provides global payments and financial technology, solutions. The company offers a global payment platform that enables merchants to process online payments, optimize transaction approval rates, and utilize advanced security and anti-fraud measures. PayU primarily serves the ecommerce industry, providing financial services and payment solutions to businesses looking to expand their reach in emerging markets. It was founded in 2002 and is based in Hoofddorp, Netherlands. PayU operates as a subsidiary of Naspers.

BlueSnap, formerly Plimus, is a flexible payment solutions provider delivering a customizable platform to global online businesses such as software publishers, web hosting companies, and online retailers. BlueSnap builds and manages online businesses for software publishers, web hosting companies and online retailers. A business can choose BlueSnap hosted application that spans the entire e-Commerce lifecycle, or it can deploy the BlueSnap API which allows retailers to integrate the technology with existing solutions. Using BlueSnap software, retailers can deliver newsletters to customers, coupons and promotions, realtime reporting, and live chat amongst other features.
Planet Payment specializes in tax-free shopping services and (Value Added Tax) VAT refund solutions within the retail and hospitality sectors. The company offers a VAT refund service for international shoppers and provides businesses with end-to-end payment solutions and tax-free refund processes. Planet Payment was formerly known as Fintrax. It was founded in 1985 and is based in Galway, Ireland.
InComm Payments specializes in innovative payment technology solutions. The company offers a range of products including frictionless payment options, alternative payment methods like cryptocurrency, and management services for healthcare benefits. InComm Payments primarily serves sectors such as retail, healthcare, and e-commerce with its technology. It was founded in 1992 and is based in Atlanta, Georgia.
Loading...