
Phantom
Founded Year
2021Stage
Series B | AliveTotal Raised
$118.5MValuation
$0000Last Raised
$109M | 3 yrs agoMosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
-102 points in the past 30 days
About Phantom
Phantom is a multi-chain crypto wallet company that operates in the blockchain and cryptocurrency sectors. The company offers a wallet that supports multiple blockchain networks, allows for NFT transactions, and provides tools for token swapping and staking with a focus on user security and privacy. Phantom's wallet is designed to be a self-custodial solution with additional features such as scam detection and hardware wallet integration. It was founded in 2021 and is based in San Francisco, California.
Loading...
ESPs containing Phantom
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The crypto wallets market offers users a secure and convenient way to store, manage, and transfer their cryptocurrencies. These digital wallets can be accessed through mobile devices or web applications, providing users with easy access to their assets at any time. With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies, the demand for crypto wallets is also growing. As more businesses and projects ado…
Phantom named as Leader among 15 other companies, including Coinbase, Ledger, and Blockchain.
Loading...
Research containing Phantom
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Phantom in 1 CB Insights research brief, most recently on Jul 29, 2022.

Jul 29, 2022
Where a16z is investing in crypto and blockchainExpert Collections containing Phantom
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Phantom is included in 2 Expert Collections, including Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups.
Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups
1,244 items
Blockchain
14,776 items
Companies in this collection build, apply, and analyze blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies for business or consumer use cases. Categories include blockchain infrastructure and development, crypto & DeFi, Web3, NFTs, gaming, supply chain, enterprise blockchain, and more.
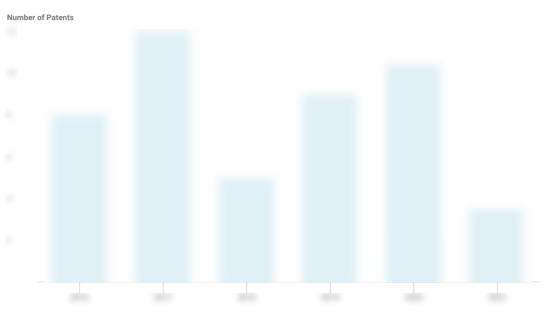
Phantom Patents
Phantom has filed 8 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- biotechnology
- gene delivery
- immunology
Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
3/26/2021 | 5/23/2023 | Radiation therapy, Medical physics, Medical imaging, Radiobiology, Magnetic resonance imaging | Grant |
Application Date | 3/26/2021 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 5/23/2023 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Radiation therapy, Medical physics, Medical imaging, Radiobiology, Magnetic resonance imaging |
Status | Grant |
Latest Phantom News
Sep 19, 2024
Too Long; Didn't Read This section evaluates several DAG-based blockchain protocols, focusing on vulnerabilities to incentive attacks, where greedy miners deviate from the RTS strategy. The analysis covers key protocols like Inclusive, PHANTOM, GHOSTDAG, and Prism, illustrating how these deviations can affect transaction throughput and mining rewards. DAG-ORIENTED SOLUTIONS In this section, we briefly review a few DAG-PROTOCOLs potentially vulnerable to the incentive attacks we are investigating. Inclusive Protocol. Lewenberg et al. [26] proposed a new way to structure the chain that can operate at much faster rates than Bitcoin. The authors utilize the DAG to form blocks in a structure called the blockDAG. This structure is created by allowing blocks to reference multiple previous blocks, enabling less strict transaction inclusion rules that can potentially store conflicting transactions in parallel blocks due to allowing λ < τ . This means that the system can process larger blocks faster than is possible to gossip within the bounds of τ , allowing for an increase in transaction throughput. The authors propose the protocol as a building block for other DAG-oriented protocols, and they claim that they reduce the advantage of highly connected miners in single-chain protocols since even stale blocks (of a single-chain) are included. Further, the authors present the key concept of randomly selecting transactions (i.e., RTS) to avoid collisions; however, according to their definition, the random selection does not necessarily equals to uniformly random selection. The authors theoretically analyze this assumption by modeling the protocol and its transaction selection as a game, in which rational miners opt to avoid collisions. According to the authors, the game’s outcome is a sequential equilibrium, where the growing fraction of greedy miners causes a decrease in their profits, which should make such a strategy less attractive (we show this phenomenon in Fig. 6). However, the authors do not assume that the miners can create a mining pool, in which they can achieve significantly higher profits than honest miners (we demonstrate it in Fig. 7a). PHANTOM. The PHANTOM protocol [44] is a generalization of the NC’s longest-chain protocol. While in NC each block contains a hash of the previous block in the chain it extends, PHANTOM organizes blocks in a DAG. As a result, each block may contain multiple hash references to predecessors, like in Inclusive [26] that is the bases for PHANTOM. The key contribution of PHANTOM is that it totally orders all blocks by solving the maximum k-cluster SubDAG problem, which utilizes the concept of the main chain and the distance from it. Unlike NC which discards the blocks out of the main chain (i.e., orphan blocks), PHANTOM includes these blocks in a DAG, except for the attacker-created blocks that would be weakly connected to DAG. PHANTOM uses the RTS strategy proposed by the (partially overlapping) authors of the Inclusive protocol. The incentive scheme of PHANTOM revolves around rewarding all miners who include a transaction within a new block A, while assuming that transactions in the parallel blocks are unique and due to a DAG will not be discarded as in single-chain blockchains. If there are some duplicate transactions, PHANTOM rewards them only once – in the first block that includes them, which is evaluated after establishing the total ordering. However, such an incentive scheme must be constructed with care, as sidechain blocks might also be the result of an attack. Therefore, the reward a miner receives for publishing A is indirectly proportional to the discretized delay at which A was referenced by the main chain. For this reason, the protocol defines a measure of the delay in publishing A w.r.t. the main chain, called the gap parameter c. The value by which the reward is “decayed” is determined by the discount function γ, where γ(c(A)) ∈ [0, 1] and γ is weakly decreasing. [6] Finally, the miner is rewarded for including transactions in A using the payoff function. In detail, the miner gets rewarded for all nonduplicate transactions contained in A, and after γ was applied to the respective transaction fees. GHOSTDAG. PHANTOM is considered impractical for efficient use [44], because it requires the solution of an NPhard problem (the maximum k-cluster SubDAG problem). Therefore, the authors of PHANTOM have developed a greedy (heuristic) algorithm to find block clusters, obtaining the GHOSTDAG protocol. This protocol uses greedy ordering of the DAG, which has practical advantages. Kaspa. The RTS strategy is utilized even in the already running blockchain Kaspa [42], which is the implementation of the GHOSTDAG protocol. Kaspa selects transactions using a variant of the RTS strategy, in which a small fraction of a block is dedicated to prioritized transactions with higher fees and remaining part of a block serves for transactions selected uniformly at random. We argue that even this approach is vulnerable to our incentive attacks since the part of the block relying on uniformly random selection cannot be enforced/verified, and thus miners might still prioritize transactions with higher fees, which can consequently result in throughput problems and incentive attacks. Nevertheless, the current Kaspa mainnet is not saturated, and its blocks usually contain only 1 to 5 transactions,[7] not fully utilizing the concept of DAG for increased throughput. Prism. Prism [6] is a protocol that aims to achieve a total ordering of transactions with consistency and liveness guarantees while achieving high throughput and low latency. Prism differs from traditional single-chain blockchains since it involves a few parallel chains rather than a single chain. It decouples transaction confirmation, validation, and proposal, whereas these processes are traditionally tightly coupled. Prism replaces traditional blocks with (1) transaction blocks (i.e., blocks that contain transactions), (2) voter blocks (i.e., blocks that vote for proposer blocks), and (3) proposer blocks (i.e., blocks that reference transaction blocks). The authors of Prism recognize that blocks mined in parallel chains might contain duplicate transactions. To cope with this problem, they propose to randomly divide unprocessed transactions of the local mempool into multiple queues and then create blocks using transactions only from one randomly selected queue, which is a variant of RTS strategy and thus enables incentive attacks based on greedy strategy. However, the authors do not provide any analysis related to such incentive attacks. Authors:
Phantom Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Phantom founded?
Phantom was founded in 2021.
Where is Phantom's headquarters?
Phantom's headquarters is located at 447 Sutter Street #405, San Francisco.
What is Phantom's latest funding round?
Phantom's latest funding round is Series B.
How much did Phantom raise?
Phantom raised a total of $118.5M.
Who are the investors of Phantom?
Investors of Phantom include Andreessen Horowitz, Jump Capital, Variant Fund, Paradigm, Solana Ventures and 6 more.
Who are Phantom's competitors?
Competitors of Phantom include Demox Labs and 3 more.
Loading...
Compare Phantom to Competitors
MetaMask is a company that operates in the blockchain technology sector, focusing on providing digital wallet services. The company offers a crypto wallet that allows users to buy, store, send, and swap digital tokens, including NFTs, and serves as a gateway to blockchain applications. It primarily caters to the decentralized finance (DeFi) and web3 sectors. It is based in San Francisco, California.

Rainbow is a company that specializes in providing secure and user-friendly cryptocurrency wallets for the Ethereum blockchain. Their products include a mobile wallet app for iOS and Android, as well as a browser extension that offers quick and versatile on-chain actions. The company caters to both individual users and the broader cryptocurrency community with features like NFT management, cross-chain swaps, and hardware wallet support. It was founded in 2018 and is based in Brooklyn, New York.
Blockchain Worx operates as a technology innovator focused on harnessing Web3 and Blockchain technology for Digital Transformation. The company offers turnkey solutions that enable organizations to create next-generation digital finance and regulatory systems, including a framework for digital banking, a platform for tokenized securities, and an application for anti-money laundering. Blockchain Worx primarily serves the financial technology and regulatory technology industries. It was founded in 2017 and is based in Singapore.
Accubits Technologies is a technology company that focuses on artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies in the software development and technology consulting industry. The company offers a range of services including AI development, blockchain development, product development, technology consulting, and enterprise solutions. These services are designed to help businesses automate processes, gain real-time insights, improve customer experiences, and optimize operations for better efficiency and profitability. It was founded in 2012 and is based in Vienna, Virginia.

BlockApps specializes in blockchain technology, focusing on the tokenization of real-world assets within various sectors. The company offers a digital marketplace where users can securely buy, sell, and trade items such as luxury goods, metals, and carbon offsets using blockchain-based tokens. BlockApps primarily serves individuals and businesses looking to engage in Web3Commerce with tangible assets. It was founded in 2015 and is based in Brooklyn, New York.
Taurus delivers enterprise infrastructural management services. The company's products include Taurus Protect, Taurus Explorer, Taurus Capital, and more. It covers issuance, custody, asset servicing, and trading facilities. Taurus primarily serves the banking and financial institutions sector. The company was founded in 2018 and is based in Geneva, Switzerland.
Loading...