
Redis
Founded Year
2011Stage
Series G | AliveTotal Raised
$355MValuation
$0000Last Raised
$110M | 3 yrs agoMosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
-50 points in the past 30 days
About Redis
Redis is a real-time data platform focused on providing in-memory data structure storage and enterprise scaling solutions. The company offers products such as an in-memory database for caching and streaming, a fully managed cloud service integrated with major cloud providers, and self-managed software designed for enterprise needs. Redis primarily serves sectors that require high-performance data operations, such as financial services, gaming, healthcare, and retail. It was founded in 2011 and is based in Mountain View, California.
Loading...
ESPs containing Redis
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The NoSQL database market revolves around the development, provision, and adoption of non-relational database management systems. NoSQL databases are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data, offering scalability, high performance, and flexibility compared to traditional relational databases. The market encompasses a variety of NoSQL database technologies, including…
Redis named as Outperformer among 15 other companies, including Microsoft Azure, Oracle, and Cloudera.
Loading...
Expert Collections containing Redis
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Redis is included in 3 Expert Collections, including Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups.
Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups
1,244 items
Conference Exhibitors
5,302 items
Tech IPO Pipeline
257 items
The tech companies we think could hit the public markets next, according to CB Insights data.
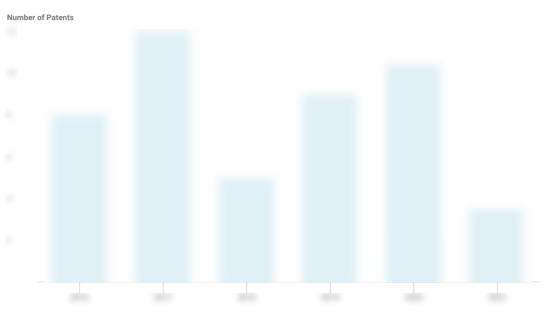
Redis Patents
Redis has filed 15 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- database management systems
- data management
- databases
Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
5/9/2023 | 7/23/2024 | Computer memory, Database management systems, Data management, SDRAM, Databases | Grant |
Application Date | 5/9/2023 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 7/23/2024 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Computer memory, Database management systems, Data management, SDRAM, Databases |
Status | Grant |
Latest Redis News
Sep 20, 2024
TechBullion In today’s data-driven world, selecting the right database is essential for any organization aiming to optimize performance, scalability, and functionality. With the increasing complexity of applications and the diverse nature of data, understanding database solutions has become more crucial than ever. Madhu Garimilla, an expert, highlights the need for organizations to navigate the evolving database landscape thoughtfully, ensuring they align their database choices with their specific requirements. The Evolving Database Landscape Global data volume is expanding rapidly, with the International Data Corporation predicting it will reach 175 zettabytes by 2025. This surge in data requires a structured approach to database selection, with options ranging from traditional relational databases to newer NoSQL and NewSQL solutions. Relational databases like Oracle, MySQL, and PostgreSQL remain industry standards due to their strong consistency, ACID compliance, and robust ecosystems. However, the need for scalability and flexibility in handling unstructured data has driven the adoption of NoSQL databases like MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis, which offer improved performance at the expense of some consistency. A key innovation is the emergence of NewSQL databases, such as Google Spanner and CockroachDB, which aim to combine the best of relational and NoSQL systems by providing both scalability and strong consistency. NewSQL databases leverage distributed architectures and consensus algorithms to provide flexible solutions while maintaining ACID properties. This allows them to combine the scalability of NoSQL systems with the reliability of traditional relational databases. Aligning Database Choices with Organizational Needs The first critical step in selecting a database is defining the project’s specific requirements, including data structure, data model, and application read-write patterns. Relational databases, like MySQL, excel in managing highly structured data with strict organization, making them ideal for applications requiring defined relationships. For semi-structured or unstructured data, NoSQL databases or data lakes, like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage, offer greater flexibility. MongoDB, for instance, is suited for document-based data models, while Apache Cassandra handles large datasets with high throughput. Understanding the data model is crucial, as it defines the logical structure and relationships between data elements. Relational databases work well for complex relationships, whereas NoSQL databases offer flexibility for dynamic data environments. Databases are also optimized for specific transactions—Cassandra is excellent for high-frequency reads, while MongoDB is preferred for write-heavy applications, ensuring performance without sacrificing availability. Clear alignment between database selection and application needs is essential for operational success. Innovations in Analytical and Specialized Databases Specialized databases are emerging to address specific industries and use cases. Analytical databases like ClickHouse, Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery excel at large-scale data analysis and real-time processing, supporting business intelligence applications with features like columnar storage and parallel processing for handling complex queries. Industry-specific databases are also gaining traction—graph databases like Neo4j optimize complex relationships, while GPU databases such as OmniSci use GPU acceleration for high-performance analytics. In AI and machine learning, vector databases like Pinecone are essential for managing high-dimensional vector data used in recommendation engines and AI solutions. Operational Considerations and Proof of Concepts Once the core requirements and features are identified, organizations must evaluate the operational aspects of each database option. Integration with existing technology stacks is a key consideration, especially in environments that rely on popular programming languages and frameworks. Cloud-based managed databases have become increasingly popular due to their scalability and ease of deployment, reducing the burden on internal teams. It’s also recommended to conduct proof of concepts (POCs) or benchmarks before finalizing a database. This step allows organizations to evaluate real-world performance, scalability, and the suitability of selected options. By simulating actual workloads, they can ensure the database aligns with both technical and business requirements, leading to optimal performance. Benchmarking quantitatively measures database performance across workloads, using standards like TPC-C and TPC-H to compare different databases. To wrap up, in the complex and rapidly evolving world of data management, selecting the right database is more important than ever. As Madhu Garimilla expertly outlines, a structured methodology can guide organizations through this process, ensuring that database choices align with performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness goals. Whether navigating the world of relational, NoSQL, NewSQL, or specialized databases, organizations must prioritize their unique requirements to stay ahead in a data-driven world.
Redis Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Redis founded?
Redis was founded in 2011.
Where is Redis's headquarters?
Redis's headquarters is located at 700 East El Camino Real, Mountain View.
What is Redis's latest funding round?
Redis's latest funding round is Series G.
How much did Redis raise?
Redis raised a total of $355M.
Who are the investors of Redis?
Investors of Redis include Technology Crossover Ventures, Tiger Global Management, SoftBank, Softbank Capital, Viola Ventures and 10 more.
Who are Redis's competitors?
Competitors of Redis include Aerospike, MarkLogic, SingleStore, DataStax, Imply and 7 more.
Loading...
Compare Redis to Competitors

Cloudera operates as a company focused on data management and analytics in the technology sector. It offers a hybrid data platform that enables secure data management and portable cloud-native data analytics, allowing businesses to transform complex data into clear and actionable insights. It primarily serves sectors such as financial services, telecommunications, public sector, retail, insurance, manufacturing, healthcare, and education. The company was founded in 2008 and is based in Santa Clara, California.

DataStax specializes in providing a comprehensive generative AI stack for the development and deployment of production-ready applications within the technology sector. The company offers a RAG API that supports both vector and structured data, ensuring secure, compliant, and scalable solutions that are integrated with leading AI ecosystem partners. DataStax primarily caters to developers and enterprises looking to leverage generative AI technologies across various cloud platforms. It was founded in 2010 and is based in Santa Clara, California.

SingleStore provides real-time analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) solutions in the data management industry. The company offers a distributed SQL database that supports both transactional and analytical workloads, enabling data-intensive applications to operate with simplicity, speed, and scale. It primarily serves digital giants and leading SaaS providers. It was formerly known as MemSQL. It was founded in 2011 and is based in San Francisco, California.

CrateDB operates as an enterprise database optimized for time series, documents, and vector data workloads. The company offers a distributed structured query language (SQL) database that enables complex queries on various data types and integrates with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) frameworks. It primarily serves sectors that require real-time analytics and data management, such as AI/ML industries. The company was founded in 2013 and is based in Redwood City, California.
Fauna operates as a document-relational database delivering a cloud-based application programming interface (API) platform. It provides a database for social and mobile applications. Its solutions include security models, event streaming, programming interfaces, data import, developer tooling, and more. It was founded in 2015 and is based in San Mateo, California.
ArangoDB is a company that focuses on providing graph database solutions in the technology sector. The company offers a scalable graph database platform, ArangoGraph Insights Platform, that enables data analytics and uncovers insights in complex data architectures, suitable for use cases such as fraud detection, supply chain management, network analysis, and more. ArangoDB primarily serves industries such as financial services, healthcare, and telecommunications. It was founded in 2014 and is based in San Mateo, California.
Loading...